Solar power generator for off grid living – Solar power generator for off-grid living is gaining significant traction as more individuals seek energy independence. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of solar generators available, from portable units ideal for RVs to fixed-mount systems suited for remote cabins. We delve into system components, installation best practices, battery selection and maintenance, and crucial safety considerations. Ultimately, we aim to empower readers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about embracing off-grid living powered by the sun.
The transition to off-grid living presents unique challenges, but harnessing solar power offers a sustainable and increasingly affordable solution. This guide will walk you through the process, from assessing your energy needs and selecting the appropriate system components to understanding the long-term cost savings and potential return on investment. We’ll cover everything from basic system setup to advanced power management techniques, ensuring you’re well-equipped to navigate the world of off-grid solar energy.
Types of Solar Power Generators for Off-Grid Living
Choosing the right solar power generator is crucial for successful off-grid living. The ideal system depends heavily on your energy needs, budget, and the specific location of your off-grid dwelling. Three main types cater to different off-grid scenarios: portable, fixed-mount, and hybrid systems.
Portable Solar Generators
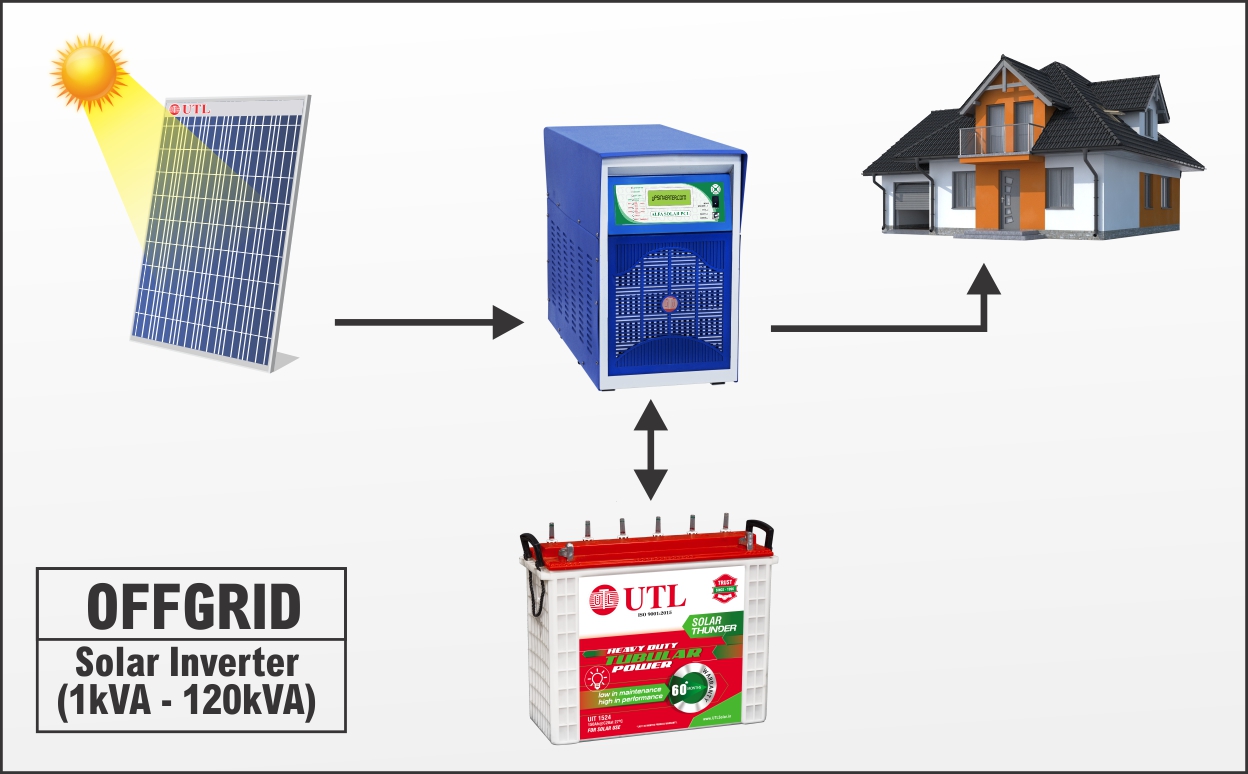
Source: upsinverter.com
Solar power generators are essential for successful off-grid living, providing reliable energy for various needs. This is especially crucial for those embracing self-sufficiency, such as individuals involved in off grid living gardening , where power is needed for irrigation systems and other gardening tools. Ultimately, a robust solar setup ensures a sustainable and productive lifestyle for off-grid homesteaders.
Portable solar generators are ideal for smaller off-grid applications or as supplemental power sources. They are typically characterized by their compact size and ease of transport. These units often integrate solar panels, batteries, and an inverter into a single, self-contained unit. Wattage typically ranges from 300W to 3000W, with battery capacities varying from a few hundred watt-hours to several kilowatt-hours.
Most use modified sine wave inverters, suitable for most appliances but potentially less efficient for sensitive electronics.
Fixed-Mount Solar Power Systems, Solar power generator for off grid living
Fixed-mount systems are designed for larger off-grid homes or cabins where portability isn’t a primary concern. These systems typically consist of separate components: solar panels mounted on a roof or stand, a charge controller, a battery bank, and an inverter. They offer higher power output and greater scalability compared to portable generators. Wattage can reach tens of kilowatts, with battery capacities ranging from several kilowatt-hours to tens of kilowatt-hours.
Pure sine wave inverters are commonly used, ensuring compatibility with all appliances and electronics.
Hybrid Solar Power Systems
Hybrid systems combine the advantages of both portable and fixed-mount systems. They typically include a fixed-mount solar array for primary power generation, supplemented by a portable generator or battery backup for cloudy days or peak demand periods. This provides greater reliability and resilience during periods of low solar irradiance. These systems offer flexibility in terms of power output and battery capacity, adapting to diverse energy needs.
| Feature | Portable | Fixed-Mount | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wattage | 300W – 3000W | kW – tens of kW | Variable, depending on components |
| Battery Capacity | Few hundred Wh – several kWh | Several kWh – tens of kWh | Variable, depending on components |
| Inverter Type | Modified sine wave (mostly) | Pure sine wave (mostly) | Variable, depending on components |
| Portability | High | Low | Medium (depending on portable component) |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost | Moderate to high initial cost |
| Suitability | Tiny homes, RVs, camping | Off-grid homes, cabins | Larger off-grid homes, needing backup power |
System Components and Setup
A typical off-grid solar power system comprises several key components working in concert. Understanding their roles and interconnections is essential for proper system design and installation.
Essential Components and Safe Installation
The core components include: solar panels (converting sunlight to DC electricity), a charge controller (regulating the flow of electricity from panels to batteries), batteries (storing energy), an inverter (converting DC to AC electricity for appliances), and wiring (connecting all components safely). Proper wiring diagrams and adherence to safety regulations are crucial during installation to prevent electrical hazards. A qualified electrician is recommended for complex installations.
Wiring Diagram (Simplified): A typical setup involves connecting solar panels in series or parallel to increase voltage or current, respectively. The output from the panels feeds into the charge controller, which then charges the batteries. The batteries provide DC power to the inverter, which converts it to AC power for household use.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
- Assess energy needs: Determine your daily energy consumption to size the system appropriately.
- Choose components: Select solar panels, batteries, charge controller, and inverter based on your needs and budget.
- Mount solar panels: Install the panels in a location with optimal sun exposure.
- Wire the system: Connect the panels to the charge controller, controller to batteries, and batteries to the inverter, adhering to safety regulations and using appropriate wire gauges.
- Test the system: Verify all connections and ensure the system is functioning correctly.
Battery Selection and Maintenance
Battery technology significantly impacts the performance, lifespan, and cost of your off-grid solar system. Careful selection and regular maintenance are essential for maximizing battery life and system efficiency.
Battery Technologies and Sizing
Lead-acid batteries are a cost-effective option but have shorter lifespans and require more maintenance compared to lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive upfront but offer longer lifespans, higher energy density, and require less maintenance. Battery sizing depends on energy consumption and desired autonomy (how long the system can operate without sunlight). For example, a household using 5 kWh daily and requiring 3 days of autonomy would need a 15 kWh battery bank.
Battery Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including checking electrolyte levels (for lead-acid batteries), keeping terminals clean, and monitoring voltage levels, extends battery life. Avoid deep discharging, which can damage batteries. For lithium-ion batteries, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for charging and discharging is critical.
Power Management and Energy Efficiency
Efficient power management is key to maximizing the lifespan of your off-grid solar system and minimizing energy waste. Adopting energy-saving practices can significantly reduce your energy consumption and extend the life of your batteries.
Energy Audit Checklist
A thorough energy audit helps identify areas for improvement. Consider aspects such as insulation levels, appliance efficiency, lighting choices, and heating/cooling systems. An example checklist might include:
- Insulation levels in walls, roof, and floors
- Energy efficiency ratings of appliances
- Use of LED lighting
- Efficiency of heating and cooling systems
- Water heating efficiency
Energy Conservation Tips
Simple strategies like using energy-efficient appliances, turning off lights when leaving a room, and minimizing the use of energy-intensive appliances during peak sunlight hours can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Cost Considerations and Return on Investment: Solar Power Generator For Off Grid Living
The initial investment in an off-grid solar power system can be substantial, but the long-term cost savings compared to grid electricity can make it a worthwhile investment. A thorough cost analysis, including equipment, installation, and maintenance, is crucial for determining the return on investment.
Cost Breakdown
Costs vary depending on system size and location. Typical costs include solar panels, batteries, charge controller, inverter, wiring, installation labor, and potentially permits. A basic system might cost several thousand dollars, while larger systems can cost tens of thousands.
| Cost Item | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | $1000 – $5000 |
| Batteries | $1000 – $10000+ |
| Charge Controller | $100 – $500 |
| Inverter | $200 – $2000+ |
| Installation | $500 – $2000+ |
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI is calculated by dividing the net savings (total savings minus initial investment) by the initial investment. The timeframe for achieving positive ROI depends on factors such as electricity prices, system size, and equipment lifespan. For example, a system costing $10,000 that saves $1500 annually would have a simple payback period of approximately 6.7 years.
Safety Precautions and Regulations
Off-grid solar power systems, while beneficial, present potential safety hazards if not installed and maintained correctly. Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is paramount.
Safety Hazards and Preventative Measures
Potential hazards include electric shock, fire, and exposure to UV radiation. Preventative measures include using appropriate safety equipment during installation, grounding the system properly, using surge protectors, and regularly inspecting wiring for damage. Proper ventilation is essential to prevent overheating, especially for battery banks.
Safety Regulations and Emergency Procedures
Local building codes and electrical regulations govern the installation of solar power systems. Consult with local authorities to ensure compliance. In case of system malfunctions or power outages, disconnect the system from the load and contact a qualified electrician for repairs. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe operation and maintenance.
Off-Grid Living Scenarios and System Sizing
The size and type of solar power system required vary significantly depending on the specific off-grid living scenario. Careful consideration of energy needs is crucial for proper system design.
System Sizing for Different Scenarios
A small cabin with minimal energy needs might require a smaller system compared to a large off-grid home with numerous appliances. Factors to consider include the number of occupants, appliance usage, and desired level of autonomy. For example, a small cabin might need a 2kW system, while a larger home might require a 10kW system or more.
Calculating Energy Needs
Calculate the energy needs of individual appliances by multiplying their wattage by the number of hours of daily use. Summing the energy needs of all appliances provides a total daily energy consumption. This information, combined with desired autonomy, is used to determine the size of the solar array and battery bank.
Last Recap
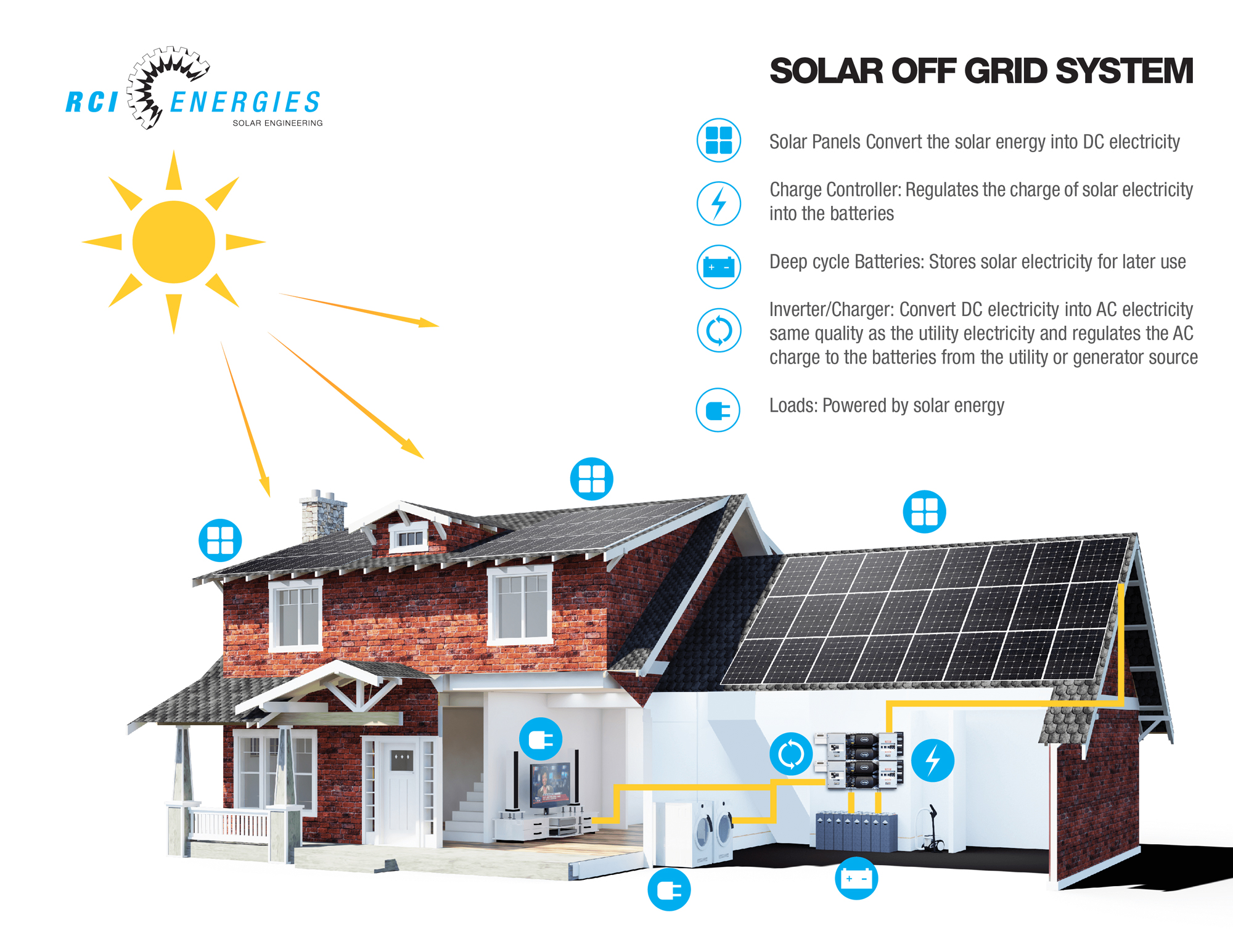
Source: com.au
Embracing off-grid living powered by solar energy represents a significant step towards self-sufficiency and environmental responsibility. While the initial investment may seem substantial, the long-term benefits—both financial and environmental—are undeniable. By understanding the various system components, optimizing energy consumption, and adhering to safety protocols, individuals can successfully harness the power of the sun to create a comfortable and sustainable off-grid lifestyle.
This guide serves as a starting point for your journey towards energy independence, encouraging further research and personalized planning to best suit your specific needs and circumstances.
